Testing procedures for implementation of Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) in the 5GHz band
<Table No. 45 Test Methods for Radio Equipment Listed in Certification Regulations Article 2 Paragraph 1 Items 19-3 and 19-3-2 (extract)>
DFS in the 5250-5350 MHz band (for EUT with antenna terminal)
- Block diagram of measuring system
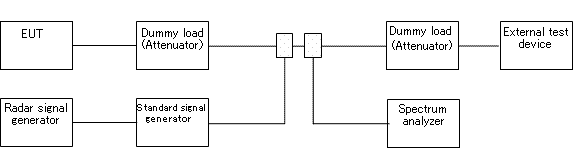
- Conditions of measuring equipment
- (i)The external test device shall be a device that can be connected to EUT through a line. The test device, however, may be replaced with an appropriate, opposed device that can communicate with EUT.
- (ii)Generate pulses based on test signals in the following table with the radar signal generator, apply them to the external pulse modulation input of the standard signal generator, and generate quasi radar pulses.
Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Fixed pulse 1 1.0 700 18 15.0 Fixed pulse 2 2.5 260 18 15.0 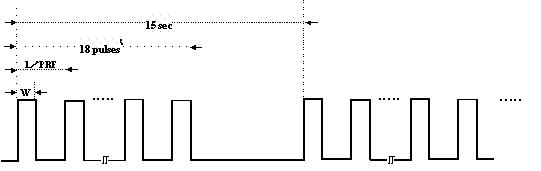
-
(iii)The standard signal generator shall be set as follows:
- Carrier frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Modulation: Signals shall be pulse-modulated with signals output from the radar signal generator
- Output level: Mean power (prescribed input level) during a period of radar wave transmission shall be set as follows in the antenna input section of EUT.
- Absolute gain of the reception antenna shall be the value declared in the application document.
- (a)When the maximum EIRP of EUT is below 200 mW;
-62 dBm + absolute gain of reception antenna (dBi)
- (b)When the maximum EIRP of EUT is 200 mW or more;
-64 dBm + absolute gain of reception antenna (dBi)
-
(iv)The spectrum analyzer shall be set as follows:
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 0 Hz
- Resolution bandwidth: Approximately 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately same as the resolution bandwidth
- Y-axis scale: 10 dB/Div
- Sweep time: Approximately 15 s
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
- Conditions of EUT
Select the test frequency at random respectively from the frequencies that EUT can emit for the tests of Steps (4)-(i)-A to -C or for those of Steps (4)-(ii)-A to -E. - Measuring procedure
Confirm operations of the dynamic frequency selection function with the test signals (fixed pulses 1 and 2) listed in (2) above as follows:-
(i)Confirming available channels
- A.Set the standard signal generator to be in non-transmission state.
- B.Set EUT to be in state of available channel checking by initializing EUT and confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT does not radiate emissions.
- C.In a time slot selected randomly from the time period of available channel checking, set the standard signal input generator to be in transmission state and apply quasi radar pulses at the prescribed level to EUT.
- D.Confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT does not radiate emissions when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT.
- E.Repeat Steps A to D four times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
-
(ii)Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Set the standard signal generator to be in non-transmission state.
- B.Set EUT to be in state of operating channel monitoring by initializing it and transmit waves at the test frequency.
- C.Set the communication load conditions for EUT so that the transmission speed for signals that do not include error correction and control signals may amount to 50% of the maximum signal transmission speed for radio equipment, and establish communications with the external test device.
- D.Set the standard signal generator to be in transmission state and apply quasi radar pulses at the prescribed input level to EUT.
- E.Confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT stops radiating emissions when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT.
- F.Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 15 times.
- G.If the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection is 11 to 14 in Step F, repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection by adding the value in Step F and the one in this step.
-
(i)Confirming available channels
- Record of measured results
- (i)Confirming available channels
- A.Describe the statue with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse four times in Step (4)-(i)-E and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse three times or less.
- B.Regarding "time period during which transmission stops when radar emissions have been detected by confirming available channels," confirm it with the application document.
- (ii)Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Indicate the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 15 times or more in Step (4)-(ii)-F and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse 10 times or less.
- B.If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-G, indicate the test result with "Pass" when EUT detected a quasi radar pulse 24 times or more and with "Fail" when it detected the pulse 23 times or less.
- C.In conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail" in A and B above, indicate the number of pulse detections and the number of tests for each of Fixed Pulse 1 and Fixed Pulse 2.
- D.Regarding "control function from master station to slave station, "operating channel monitoring function and transmission stop time," and "time period during which transmission stops when radar emissions have been detected by monitoring operating channels," confirm them with the application document.
- (i)Confirming available channels
- Others
- (i) To transmit radar emission test signals, use a radar signal generator and standard signal generator. However the signal may be produced by a signal generator that can generate the radar wave test signals.
- (ii) Confirming available channels
- A. When confirming whether EUT detects a quasi radar pulse or not, a method without using a spectrum analyzer such as confirmation with the display of EUT may be adopted.
- B. If you set EUT to be in state of available channel checking and transmit signals at a test frequency on a permanent basis, EUT must have been set with a device such as a test jig so that it can be tested. The state of EUT in this case must be such that the probability of detecting radar pulses is the same as that in the operating status of actual radio equipment.
- (iii) Monitoring of operating channel
- A.If the number of instances where a quasi radar pulse with a repetition cycle of 15 seconds has been continuously detected is 10 or less in Step (4)-(ii)-F, describe the test result with "Fail"
- B.Keep the communication load as close as possible to 50% of the maximum signal transmission speed for EUT and monitor the communication load conditions with an appropriate method.
- C.For EUT other than radio equipment that performs transmission based on IP packet transmission which packet size varies with the transmitting information contents, the test shall be conducted under a condition of communication load where the detection probability of quasi radar pulses is minimal.
- D.When confirming whether EUT detects a quasi radar pulse or not, a method without using a spectrum analyzer such as confirmation with the display of EUT may be adopted.
- E.In case that EUT transmits radio waves fixing to a test frequency in the monitoring state of operating channel, it is required to previously set the EUT using test fixtures etc to a state enabling the test in an appropriate manner. In this state, detection probability of radar pulses by the EUT shall be the same as that by the radio equipment in the actual operation.
DFS in the 5470-5725 MHz Band (for EUT with antenna terminal)
- Block diagram of measuring system
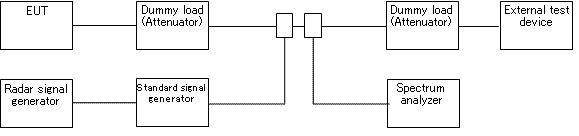
- Conditions of measuring equipment
- (i)The external test device shall be a device that can be connected to EUT through a line. The test device, however, may be replaced with an appropriate, opposed device that can communicate with EUT.
- (ii)Generate pulses based on test signals in the following tables A to D with the radar signal generator, apply them to the external pulse modulation input of the standard signal generator, and generate quasi radar pulses.
A. Fixed pulse radar wave test signals Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Fixed Pulse 1 0.5 720 18 15.0 Fixed Pulse 2 1.0 700 18 15.0 Fixed Pulse 3 2.0 250 18 15.0 B. Variable pulse radar wave test signals Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Variable
Pulse 4Width in a range of 1 to 5
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
4,347 to 6,667 HzAny one integer
between 23 and 2915.0 Variable
Pulse 5Width in a range of 6 to 10
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
2,000 to 5,000 HzAny one integer
between 16 and 1815.0 Variable
Pulse 6Width in a range of 11 to 20
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
2,000 to 5,000 HzAny one integer
between 12 and 1615.0 Note: Each item in the table shall consist of any combination of 1.
C. Charp radar wave test signal Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Charp Width in a range of 50 to 100
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
500 to 1,000 HzAny one integer
between 1 and 312.0 - Note 1: Bursts shall be transmitted within 12 seconds.
- Note 2: The charp width shall be a frequency width that ranges from 5 to 20 MHz in increments of 1 MHz.
An individual charp width can be any in each burst and charp widths within the same burst shall be equal. - Note 3: The number of bursts shall be any integer in a range of 8 to 20 and a burst interval shall be a time period derived
&nb sp;from dividing 12 seconds with the number of bursts. - Note 4: If there are multiple pulses within a burst of 1s, the width of each pulse shall be equal and the pulse repetition
frequency shall not have any relationships with that for the subsequent pulses of 1. - Note 5: Each item in the table shall consist of any combination of 1.
D. Frequency hopping radar wave test signal Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Hopping 1.0 3,000 9 10.0 - Note 1: The hopping frequency shall be any frequency that ranges from 5,250 to 5,724 MHz in increments of 1 MHz.
- Note 2: An individual hopping interval shall be 3 ms and a total of all hopping intervals shall be 300 ms.
- Note 3: Burst intervals shall be 3ms.
- Note 1:
- (iii)The standard signal generator shall be set as follows:
- Carrier frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Modulation: Signals shall be pulse-modulated with signals output from the radar signal generator.
- Output level: Mean power during a period of radar wave transmission shall be set as follows in the antenna input section of EUT.
- Absolute gain of the reception anntena shall be the value declared in the application document.
- A.When the maximum EIRP of EUT is below 200 mW
-62 dBm + absolute gain of reception antenna (dBi)
- B.When the maximum EIRP of EUT is 200 mW or more
-64 dBm + absolute gain of reception antenna (dBi)
- (iv)The spectrum analyzer shall be set as follows:
- A.When the radar signal generator is set as described in (ii)-A and -B
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 0 Hz
- Resolution bandwidth: Approximately 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately same as the resolution bandwidth
- Sweep time: Approximately 15 s
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
- B.When the radar signal generator is set as described in (ii)-C and -D
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 20 MHz or more
- Resolution bandwidth: Approximately 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately same as the resolution bandwidth
- Sweep time: Approximately 10 ms
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
- A.When the radar signal generator is set as described in (ii)-A and -B
-
Conditions of EUT
- (i)Set EUT to a test frequency and to be in state of available channel checking or to be in state of operating channel monitoring and make EUT radiate emissions.
- (ii)Select the test frequency at random from the frequencies that EUT can emit.
- (iii)Set the communication load conditions for EUT so that the transmission speed for signals that do not include error correction and control signals may amount to 17% of the maximum signal transmission speed for radio equipment.
-
Measuring Procedure
Confirm operations of the dynamic frequency selection function as follows using the test signals listed in (2) above as quasi radar pulses.
-
(i)Confirming available channels
- A.Set the output of the standard signal generator to be in non-transmission state.
- B.Set EUT to be in state of available channel checking by initializing EUT and confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT does not radiate emissions.
- C.In a time slot selected randomly from the time period of available channel checking, set the standard signal generator to be in transmission state and apply quasi radar pulses at the prescribed input level to EUT.
- D.Confirm with the spectrum analyzer whether EUT detects a quasi radar pulse when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT at first try.
- E.Repeat Steps A to D four times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not.If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
-
(ii) Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Set the standard signal generator to be in non-transmission state.
- B.Set EUT to be in state of operating channel monitoring by initializing it and transmit waves at the test frequency.
- C.Establish communications with the external test device under the prescribed communication load conditions.
- D.Set the output of the standard signal generator to be in transmission state and apply quasi radar pulses at the prescribed input level to EUT.
- E.Confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT stops radiating emissions when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT.
- F.Find the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection by following Steps (a) to (c) for test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and (2)-(ii)-B.
- (a)Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 18 times.
- (b)If the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection is 11 to 14 in Step (a), go to Step G below. If the number is 15 to 17, go to Step (c) below.
- (c)Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
- G.Find the mean of probabilities of detecting quasi radar pulses.
- (a)Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
- (b)Find a total of the numbers of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection and a total of the numbers of tests for each of six types of test signals listed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B.
-
H.Find the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection for the test signal listed in (2)-(ii)-C by following Steps (a) to (c) below.
- (a) Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 18 times.
- (b) If the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection is 15 to 17 in Step (a), go to Step (c) below.
- (c) Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. Find the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection by adding the value in Step (a) and the one in this step.
-
I.Find the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection for the test signal listed in (2)-(ii)-D by following Steps (a) to (c) below.
- (a) Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 16 times.
- (b) If the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection is 13 to 15 in Step (a), go to Step (c) below.
- (c)Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
-
(i)Confirming available channels
- Record of measured results
-
(i)Confirming available channels
- A.Describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse four times in Step (4)-(i)-E and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse three times or less.
- B.Regarding "time period during which transmission stops when radar wave have been detected by confirming available channels," confirm it with the application document.
- (ii)Monitoring of operating channel
- A.In the case of the fixed pulse and variable pulse radar wave test signals
- (a) For the six types of test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B, describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 18 times or more in Step (4)-(ii)-F-(a) and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse 10 times or less.
- (b) If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-F-(c), describe the test result with "Pass" when the total number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 32 or more and with "Fail" when it is 23 or less.
- (c) If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-G, find the detection probability with the number of instances of detecting a quasi radar pulse and the number of tests for each of the six types of test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B. Then, describe the test result with "Pass" when the mean detection probability is 80% or more and with "Fail" when it is less than 80%.
- (d) In (a) to (c) above, describe the number of pulse detections and the number of tests for each of the test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B in conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail"
-
B.In the case of the charp radar wave test signal
- (a)Describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 18 times or more in Step (4)-(ii)-H-(a) and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse 14 times or less.
- (b)If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-H-(c), describe the test result with "Pass" when the total number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 32 or more and with "Fail" when it is 31 or less.
- (c)In (a) and (b) above, describe the number of pulse detections and the number of tests in conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail"
-
C.In the case of frequency hopping radar wave test signals
- (a)Describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 16 times or more in Step (4)-(ii)-I-(a) and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse 12 times or less.
- (b)If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-I-(c), describe the test result with "Pass" when the total number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 28 or more and with "Fail" when it is 27 or less.
- (c)In (a) and (b) above, describe the number of pulse detections and the number of tests in conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail"
- A.In the case of the fixed pulse and variable pulse radar wave test signals
- (iii)Monitoring of operating channel
Regarding "control function from master station to slave station, "operating channel monitoring function and transmission stop time," and "time period during which transmission stops when radar wave have been detected by monitoring operating channels," confirm them with the application document.
-
(i)Confirming available channels
- Others
- (i)To transmit radar wave test signals, use a radar signal generator and standard signal generator. If it is possible to directly output radar wave test signals, however, an arbitrary waveform generator may be used.
- (ii) Confirming available channels
- A.When confirming whether EUT detects a quasi radar pulse or not, a method without using a spectrum analyzer such as confirmation with the display of EUT may be adopted.
- B.If you set EUT to be in state of available channel checking and transmit signals at a test frequency on a permanent basis, EUT must have been set with a device such as a test jig so that it can be tested. The state of EUT in this case must be such that the probability of detecting radar pulses is the same as that in the operating status of actual radio equipment.
- C.Regarding Fixed Pulse 1 and Fixed Pulse 2 in (2)-(ii)-A, tests for either pulse type may be omitted. If sampling intervals during which EUT detects radar wave exceed 0.5 µs, however, tests for Fixed Pulse 1 must be performed.
- D.Regarding Variable Pulse 5 and Variable Pulse 6 in (2)-(ii)-B, tests for either pulse type may be omitted.
- (iii) Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Keep the communication load as close as possible to 17% of the maximum signal transmission speed for EUT and monitor the communication load conditions with an appropriate method.
- B.In the case of EUT other than those that conduct transmission based on IP packet transmission, when testing such EUT, set the communication load conditions for the EUT so that the probability of detecting a quasi radar pulse is minimized.
- C.When confirming whether EUT detects a quasi radar pulse or not, a method without using a spectrum analyzer such as confirmation with the display of EUT may be adopted.
- D.If you set EUT to be in state of available channel checking and transmit signals at a test frequency on a permanent basis, EUT must have been set with an appropriate method using a device such as a test jig so that it can be tested. The state of EUT in this case must be such that the probability of detecting radar pulses is the same as that in the operating status of actual radio equipment.
- E.In the case of fixed pulse and variable pulse radar emission test signals, describe the test result with "Fail" if the number of instances where a quasi radar pulse with a repetition cycle of 15 seconds has been continuously detected is 10 or less in Step (4)-(ii)-E.
- F.In the case of a charp radar wave test signal, describe the test result with "Fail" if the number of instances where a quasi radar pulse with a repetition cycle of 12 seconds has been continuously detected is 14 or less in Step (4)-(ii)-E.
- G.In the case of a frequency hopping wave test signal, describe the test result with "Fail" if the number of instances where a quasi radar pulse with a repetition cycle of 0 second has been continuously detected is 12 or less in Step (4)-(ii)-E.
- H.Regarding Fixed Pulse 1 and Fixed Pulse 2 in (2)-(ii)-A, tests for either pulse type may be omitted. If sampling intervals during which EUT detects radar wave exceed 0.5 µs, however, tests for Fixed Pulse 1 must be performed.
- I.Regarding Variable Pulse 5 and Variable Pulse 6 in (2)-(ii)-B, tests for either pulse type may be omitted.
- J.A total of pulse detections and a total of tests in Step (4)-(ii)-G-(b) may be replaced with the totals of those for Fixed Pulse 1 or Fixed Pulse 2, those for Variable Pulse 3, those for Variable Pulse 4, and those for Variable Pulse 5 or Variable Pulse 6.
DFS in the 5250-5350 MHz band (for EUT with built-in antenna)
- Block diagram of measuring system
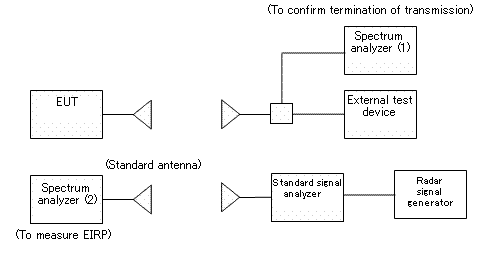
- Conditions of measuring equipment
- (i)The external test device shall be a device that can be connected to EUT through a line. The test device, however, may be replaced with an appropriate, opposed device that can communicate with EUT.
- (ii)Generate pulses based on test signals in the following table with the radar signal generator, apply them to the external pulse modulation input of the standard signal generator, and generate quasi radar pulses.
Test signal Pulse width
[µs]Pulse repetition
frequency [Hz]Number of
continuous pulsesRepetition
cycle [s]Fixed pulse 1 1.0 700 18 15.0 Fixed pulse 2 2.5 260 18 15.0 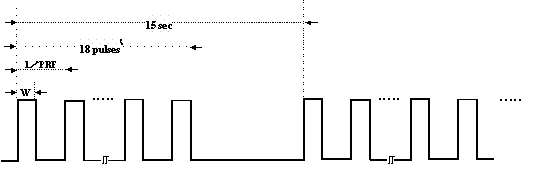
- (iii)The standard signal generator shall be set as follows:
- Carrier frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Modulation: Signals shall be pulse-modulated with signals output from the radar signal generator.
- Output level: Set the EIRP received with the reception antenna of EUT (mean power during a period of radar wave transmission: prescribed input level) as follows:
- A.When the maximum EIRP of EUT is below 200 mW;
-62 dBm
- B.When the maximum EIRP of EUT is 200 mW or more;
-64 dBm
- (iv)Spectrum analyzer (2) shall be set as follows when measuring values for EIRP in quasi radar pulse signals:
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 0 Hz
- Resolution bandwidth: 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately 3 times the resolution bandwidth
- Sweep time: Minimum time during which measurement accuracy is ensured
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
- (v)Spectrum analyzer (1) shall be set as follows when confirming that EUT stops transmission signals:
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 0 Hz
- Resolution bandwidth: Approximately 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately same as the resolution bandwidth
- Sweep time: Approximately 15 s
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
- Conditions of EUT
Select the test frequency at random respectively from the frequencies that EUT can emit for the tests of Steps (4)-(i)-A to H or for those of Steps (4)-(ii)-A to F. - Measuring procedure
Confirm operations of the dynamic frequency selection function with the test signals (fixed pulses 1 and 2) as quasi radar pulses listed in (2) above as follows:-
(i) Confirming available channels
- A.Oppose the antenna of the standard signal generator to an antenna (whose absolute gain is known) used when measuring EIRP in terms of height and direction.
- B.Turn the radar signal generator to be in state of being modulated by connecting it to the external pulse modulation input of the standard signal generator, set the latter generator to the output that can be measured with spectrum analyzer (2), and transmit quasi radar pulse signals from the antenna.
- C.Set the spectrum analyzer based on (2)-(iv) and receive quasi radar pulse signals with the standard antenna and spectrum analyzer (2). Calculate the value of EIRP for quasi radar pulse signals by adjusting the value with correction values such as the pulse desensitivity (correction value used when converting a signal level of a quasi radar pulse measured with a spectrum analyzer into a true level). The pulse desensitivity shall be 0.5 dB when the resolution bandwidth is 1 MHz.
- D.Adjust the output of the standard signal generator so that the value of EIRP calculated in Step C that is received with the reception antenna of EUT will be equal to the prescribed input level.
- E.Set the standard signal generator to be in non-transmission state.
- F.Oppose EUT to the external test device in terms of height and direction at the same distance as that between the antenna of the standard signal generator and an antenna used to measure EIRP (hereinafter called the offset distance), set the communication load conditions for EUT so that the transmission speed for signals that do not include error correction and control signals may amount to 50% of the maximum signal transmission speed for radio equipment, and establish communications with the external test device.
- G.Set EUT to be in state of available channel checking by initializing EUT and confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT does not radiate emissions.
- H.In a time slot selected randomly from the time period of available channel checking, set the standard signal generator to be in transmission state and apply quasi radar pulses at the prescribed input level to EUT.
- I.Set the spectrum analyzer based on (2)-(iv) and confirm with spectrum analyzer (1) that EUT does not radiate emissions when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT.
- J.Repeat Steps E to I four times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
-
(ii)Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Adjust the output of the standard signal generator similarly to Step (i)-D.
- B.Set the standard signal generator to be in non-transmission state.
- C.Oppose EUT to the external test device in terms of height and direction at the offset distance, set the communication load conditions for EUT so that the transmission speed for signals that do not include error correction and control signals may amount to 50% of the maximum signal transmission speed for radio equipment, and establish communications with the external test device.
- D.Set EUT to be in state of operating channel monitoring by initializing it and transmit waves at the test frequency.
- E.Set the standard signal generator to be in transmission state and transmit quasi radar pulse signals with intensity at the prescribed input level from the antenna.
- F.Set the spectrum analyzer based on (2)-(iv) and confirm with spectrum analyzer (1) that EUT stops radiating emissions when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT.
- G.Repeat Step F 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 15 times.
- H.If the number of quasi radar pulse detections is 11 to 14 in Step G, repeat Step F 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection by adding the value obtained in Step G and the one in this step.
-
(i) Confirming available channels
- Record of measured results
-
(i) Confirming available channels
- A.Indicate the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse four times in Step (4)-(i)-J and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse three times or less.
- B.Regarding "time period during which transmission stops when radar wave have been detected by confirming available channels," confirm it with the application document.
-
(ii) Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Indicate the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 15 times or more in Step (4)-(ii)-G and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse 10 times or less.
- B.If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-H, indicate the test result with "Pass" when a total of the value obtained in Step (4)-(ii)-G and the number of quasi radar pulse detections marks 24 or more for EUT and with "Fail" when the total is 23 or less.
- C.In conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail" in A and B above, describe the number of pulse detections and the number of tests for each of Fixed Pulse 1 and Fixed Pulse 2.
- D.Regarding "control function from master station to slave station," "the time period of available channel checking," "operating channel monitoring function and transmission stop time," and "time period during which transmission stops when a radar wave has been detected by confirming available channels or by monitoring operating channels," confirm them with the application document.
-
(i) Confirming available channels
- Others
Same as 13-(6). When receiving quasi radar pulse signals with the spectrum analyzer, however, the pulse desensitivity of the spectrum analyzer shall be calculated in advance and measurement values shall be adjusted with it.
DFS in the 5470-5725 MHz band (for EUT with Built-in Antenna)
- Block diagram of measuring system
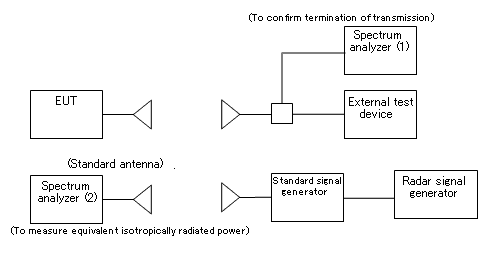
- Conditions of measuring equipment
- (i)The external test device is a device that can be connected to EUT through a line. The test device, however, may be replaced with an appropriate, opposed device that can communicate with EUT.
- (ii)Generate pulses based on test signals in the following tables A to D with the radar signal generator, apply them to the external pulse modulation input of the standard signal generator, and generate quasi radar pulses.
A. Fixed pulse radar wave test signals Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Fixed Pulse 1 0.5 720 18 15.0 Fixed Pulse 2 1.0 700 18 15.0 Fixed Pulse 3 2.0 250 18 15.0 B. Variable pulse radar wave test signals Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Variable
Pulse 4Width in a range of 1 to 5
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
4,347 to 6,667 HzAny one integer
between 23 and 2915.0 Variable
Pulse 5Width in a range of 6 to 10
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
2,000 to 5,000 HzAny one integer
between 16 and 1815.0 Variable
Pulse 6Width in a range of 11 to 20
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
2,000 to 5,000 HzAny one integer
between 12 and 1615.0 Note: Each item in the table shall consist of any combination of 1.
C. Charp radar wave test signal Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Charp Width in a range of 50 to 100
µs in increments of 1 µsAny one frequency in a range of
500 to 1,000 HzAny one integer
between 1 and 312.0 - Note 1: Bursts shall be transmitted within 12 seconds.
- Note 2: The charp width shall be a frequency width that ranges from 5 to 20 MHz in increments of 1 MHz. An individual charp width can be any in each burst and charp widths within the same burst shall be equal.
- Note 3: The number of bursts shall be any integer in a range of 8 to 20 and a burst interval shall be a time period derived from dividing 12 seconds with the number of bursts.
- Note 4: If there are multiple pulses within a burst of 1s, the width of each pulse shall be equal and the pulse
;repetition frequency shall not have any relationships with that for the subsequent pulses of 1. - Note 5: Each item in the table shall consist of any combination of 1.
D. Frequency hopping radar wave test signal Test signal Pulse width [µs] Pulse repetition frequency [Hz] Number of continuous pulses Repetition cycle [s] Hopping 1.0 3,000 9 10.0 - Note 1: The hopping frequency shall be any frequency that ranges from 5,250 to 5,724 MHz in increments of 1 MHz.
- Note 2: An individual hopping interval shall be 3 ms and a total of all hopping intervals shall be 300 ms.
- Note 3: Burst intervals shall be 3ms.
- Note 1:
- (iii)The standard signal generator shall be set as follows:
- Carrier frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Modulation: Signals shall be pulse-modulated with signals output from the radar signal generator.
- Output level: Set the EIRP received with the reception antenna of EUT (mean power during a period of radar
- wave transmission: prescribed input level) as follows:
- A.When the maximum EIRP of EUT is below 200 mW;
-62 dBm
- B.When the maximum EIRP of EUT is 200 mW or more;
-64 dBm
- (iv) Spectrum analyzer (2) shall be set as follows when measuring values for EIRP in quasi radar pulse signals:
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 0 Hz
- Resolution bandwidth: 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately 3 times the resolution bandwidth
- Sweep time: Time during which measurement accuracy is ensured
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
-
(v) Spectrum analyzer (1) shall be set as follows when confirming that EUT stops transmission signals:
-
A.When the radar signal generator is set based on (ii)-A and -B
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 0 Hz
- Resolution bandwidth: Approximately 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately same as the resolution bandwidth
- Sweep time: Approximately 15 s
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
-
B.When the radar signal generator is set based on (ii)-C and -D
- Center frequency: Center of transmission (reception) frequency band of EUT
- Frequency sweep width: 20 MHz or more
- Resolution bandwidth: Approximately 1 MHz
- Video bandwidth: Approximately same as the resolution bandwidth
- Sweep time: Approximately 10 ms
- Sweep mode: Continuous sweep
- Detection mode: Positive peak
-
A.When the radar signal generator is set based on (ii)-A and -B
- Conditions of EUT
- (i)Set EUT to a test frequency and to be in state of available channel checking or to be in state of operating channel monitoring and make EUT radiate emissions.
- (ii)Select the test frequency at random from the frequencies that EUT can emit.
- (iii)Set the communication load conditions for EUT so that the transmission speed for signals that do not include error correction and control signals may amount to 17% of the maximum signal transmission speed for radio equipment.
- Measuring procedure
Confirm operations of the dynamic frequency selection function as follows using the test signals listed in (2) above as quasi radar pulses.
- (i)Confirming available channels
- A.Oppose the antenna of the standard signal generator to the standard antenna in terms of height and direction.
- B.Turn the radar signal generator to be in state of being modulated by connecting it to the external pulse
modulation input of the standard signal generator, set the latter generator to the output that can be measured
with spectrum analyzer (2), and transmit quasi radar pulse signals from the antenna. - C.Set the spectrum analyzer based on (2)-(iv) and receive quasi radar pulse signals with the standard antenna
and spectrum analyzer (2). Calculate the value of EIRP for quasi radar pulse signals by adjusting the value
with correction values such as the pulse desensitivity. The pulse desensitivity shall be 0.5 dB when the resolution
bandwidth is 1 MHz. - D.Adjust the output of the standard signal generator so that the value of EIRP calculated in Step C that is received
with the reception antenna of EUT will be equal to the prescribed input level. - E.Set the output of the standard signal generator to be in non -transmission state.
- F.Oppose EUT to the external test device in terms of height and direction at the same offset distance as that
between the antenna of the standard signal generator and the standard antenna and establish communications
with the external test device under the prescribed communication load conditions. - G.Set EUT to be in state of available channel checking by initializing EUT and confirm with the spectrum analyzer
that EUT does not radiate emissions. - H.In a time slot selected randomly from the time period of available channel checking, set the output of the
standard signal generator to be in transmission state and apply quasi radar pulses at the prescribed input level
to EUT. - I.Confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT does not radiate emissions when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT.
- J.Repeat Steps E to I four times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not.
If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many
times it has been detected.
-
(ii)Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Adjust the output of the standard signal generator similarly to Step (i)-D.
- B.Set the output of the standard signal generator to be in non -transmission state.
- C.Set EUT to be in state of available channel checking by initializing it and confirm the state of EUT with the external test device.
- D.Establish communications with the external test device under the prescribed communication load conditions.
- E.Set the output of the standard signal generator to be in transmission state and apply quasi radar pulses at the prescribed input level to EUT.
- F.Confirm with the spectrum analyzer that EUT stops radiating emissions when quasi radar pulses are input to EUT.
- G.Find the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection for the test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and (2)-(ii)-B.
- (a)Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 18 times.
- (b)If the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 11 to 14 in Step (a), go to Step H below. If the number is 15 to 17, go to Step (c) below.
- (c)Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
- H.Find the mean of probabilities of detecting quasi radar pulses.
- (a)If the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 11 to 14 in Step G-(a), repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection.
- (b)Find a total of the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection and a total of the number of tests for each of six types of test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B.
- I.Find the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection for the test signal listed in (2)-(ii)-C as follows:
- (a)Repeat Steps B to F 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 18 times.
- (b)If the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 15 to 17 in Step (a), go to Step (c) below.
- (c)Repeat Steps B to F 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected, and find the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection by adding the value in Step (a) and the one in this step.
- J.In the case of frequency hopping radar wave test signals, find the number of occurrences of quasi radar signal detection by following Steps (a) to (c) below for the test signal prescribed in (2)-(ii)-D.
- (a)Repeat Steps B to F 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected. The measurement operation, however, shall be terminated when a quasi radar pulse has been detected 16 times.
- (b)If the number of occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 13 to 15 in Step (a), go to Step (c) below:
- (c)Repeat Steps A to E 20 times and record each time whether EUT radiates emissions or not. If EUT does not radiate emissions, assume that a quasi radar pulse has been detected and find how many times it has been detected.
- (i)Confirming available channels
- Record of measured results
- (i)Confirming available channels
- A.Indicate the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse four times in Step (4)-(i)-J and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse three times or less.
- B.Regarding "time period during which transmission stops when radar wave have been detected by confirming available channels," confirm it with the application document.
- (ii)Monitoring of operating channel
- A.In the case of fixed pulse and variable pulse radar wave test signals
- (a)For the six types of test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B, describe the test result with "Pass"
if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 18 times or more in Step (4)-(ii)-G-(a) and with "Fail"
if it has detected the pulse 10 times or less. - (b)If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-G-(c), describe the test result with "Pass" when the total number of
occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 32 or more and with "Fail" when it is 23 or less. - (c)If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-G, find the detection probability with the number of occurrences of quasi radar
pulse detection and the number of tests for each of the six types of test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A
and -B. Then, describe the test result with "Pass" when the mean detection probability is 80% or more and
with "Fail" when it is less than 80%. - (d)In (a) to (c) above, describe the number of pulse detections and the number of tests for each of the test
signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B in conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail"
- (a)For the six types of test signals prescribed in (2)-(ii)-A and -B, describe the test result with "Pass"
- B.In the case of charp radar wave test signals
- (a)Describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 18 times or more in Step
(4)-(ii)-I-(a) and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse 14 times or less. - (b)If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-I-(c), describe the test result with "Pass" when the total number of occurrences
of quasi radar pulse detection is 32 or more and with "Fail" when it is 31 or less. - (c)In conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail" in (a) and (b) above, describe the number of pulse detections
and the number of tests.
- (a)Describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 18 times or more in Step
- C. In the case of frequency hopping radar wave test signals
- (a)Describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 16 times or more in Step
(4)-(ii)-J-(a) and with "Fail" if it has detected the pulse 12 times or less. - (b)If you followed Step (4)-(ii)-J-(c), describe the test result with "Pass" when the total number of
occurrences of quasi radar pulse detection is 28 or more and with "Fail" when it is 27 or less. - (c)In conjunction with "Pass" or "Fail" in (a) and (b) above, describe the number of pulse detections
and the number of tests.
- (a)Describe the test result with "Pass" if EUT has detected a quasi radar pulse 16 times or more in Step
- A.In the case of fixed pulse and variable pulse radar wave test signals
- (iii)Monitoring channel in operation
Regarding "control function from master station to slave station, "operating channel monitoring function and transmission stop time," and "time period during which transmission stops when radar wave have been detected by monitoring operating channels," confirm them with the application document.
- (i)Confirming available channels
- Others
- (i)To transmit radar wave test signals, use a radar signal generator and standard signal generator. However, other devices that can directly output radar wave test signals, such as an arbitrary waveform generator, may be used.
-
(ii)Confirming available channels
- A.When confirming that EUT does not radiate emissions, a method such as confirmation with the display of EUT (including a test jig for display) may be adopted.
- B.When confirming whether EUT detects a quasi radar pulse or not, a method without using a spectrum analyzer such as confirmation with the display of EUT may be adopted.
- C.If you set EUT to be in state of available channel checking and transmit signals at a test frequency on a permanent basis, EUT must have been set with a device such as a test jig so that it can be tested. The state of EUT in this case must be such that the probability of detecting radar pulses is the same as that in the operating status of actual radio equipment.
- D.Regarding Fixed Pulse 1 and Fixed Pulse 2 in (2)-(ii)-A, tests for either pulse type may be omitted. If sampling intervals during which EUT detects radar wave exceed 0.5 µs, however, tests for Fixed Pulse 1 must be performed.
- E.Regarding Variable Pulse 5 and Variable Pulse 6 in (2)-(ii)-B, tests for either pulse type may be omitted.
-
(iii)Monitoring of operating channel
- A.Keep the communication load as close as possible to 17% of the maximum signal transmission speed for EUT and monitor the communication load conditions with an appropriate method.
- B.In the case of EUT other than those that conduct transmission based on IP packet transmission, when testing such EUT, set the communication load conditions for the EUT so that the probability of detecting a quasi radar pulse is minimized.
- C.When confirming whether EUT detects a quasi radar pulse or not, a method without using a spectrum analyzer such as confirmation with the display of EUT may be adopted.
- D.If you set EUT to be in state of available channel checking and transmit signals at a test frequency on a permanent basis, EUT must have been set with an appropriate method using a device such as a test jig so that it can be tested. The state of EUT in this case must be such that the probability of detecting radar pulses is the same as that in the operating status of actual radio equipment.
- E.In the case of fixed pulse and variable pulse radar wave test signals, describe the test result with "Fail" if the number of instances where a quasi radar pulse with a repetition cycle of 15 seconds has been continuously detected is 10 or less in Step (4)-(ii)-F.
- F.In the case of charp radar wave test signals, describe the test result with "Fail" if the number of instances where a quasi radar pulse with a repetition cycle of 12 seconds has been continuously detected is 14 or less in Step (4)-(ii)-F.
- G.In the case of frequency hopping radar wave test signals, describe the test result with "Fail" if the number of instances where a quasi radar pulse with a repetition cycle of 10 seconds has been continuously detected is 12 or less in Step (4)-(ii)-F.
- H.Regarding Fixed Pulse 1 and Fixed Pulse 2 in (2)-(ii)-A, tests for either pulse type may be omitted. If sampling intervals during which EUT detects radar wave exceed 0.5 µs, however, tests for Fixed Pulse 1 must be performed.
- I.Regarding Variable Pulse 5 and Variable Pulse 6 in (2)-(ii)-B, tests for either pulse type may be omitted.
- J.A total of tests in Step (4)-(ii)-G-(b) may be replaced with a total of tests for Fixed Pulse 1 or Fixed Pulse 2, those for Fixed Pulse 3, those for Variable Pulse 4, and those for Variable Pulse 5 or Variable Pulse 6. A total of pulse detections in Step (4)-(ii)-G-(b) may be replaced with a total of pulse detections for Fixed Pulse 1 or Fixed Pulse 2, those for Fixed Pulse 3, those for Variable Pulse 4, and those for Variable Pulse 5 or Variable Pulse 6.
