Mobile satellite communication is rendered from the radio station (earth station) installed in ground, maritime or air mobile entities (automobile, vessel, aircraft, etc.) to the other radio station (earth station) via the artificial satellite. (For example, it's possible to communicate (by telephone) from a ship on the Pacific Ocean to a home or an office within Japan.)
Mobile satellite communication is enabled different kinds of artificial satellites. The communicating range covers almost all the land and maritime areas in Japan. Also, mobile satellite communication is notably recognized as a powerful measure against disasters.
Based on the orbit of the satellite, it communicates by either the geostationary satellite, the quasi-zenith satellite, or the non-geostationary satellite.
1.Mobile Satellite Communication System by the Geostationary Satellite
The geostationary satellite is the artificial satellite which looks stationary from the ground. 3-4 geostationary satellites can cover almost the entire surface of the earth. Many of the artificial satellites actually used for communications or broadcasting are geostationary satellites.
- i.Altitude: about 36,000km
- ii.Orbit: the circle orbit on the equator. The cycle is the same as the earth's autorotation time.
- iii.Number of Satellites: 3-4 (service areas are duplicated.)
- iv.Principal Mobile Satellite Communications System: Inmarsat , N-STAR, Thuraya

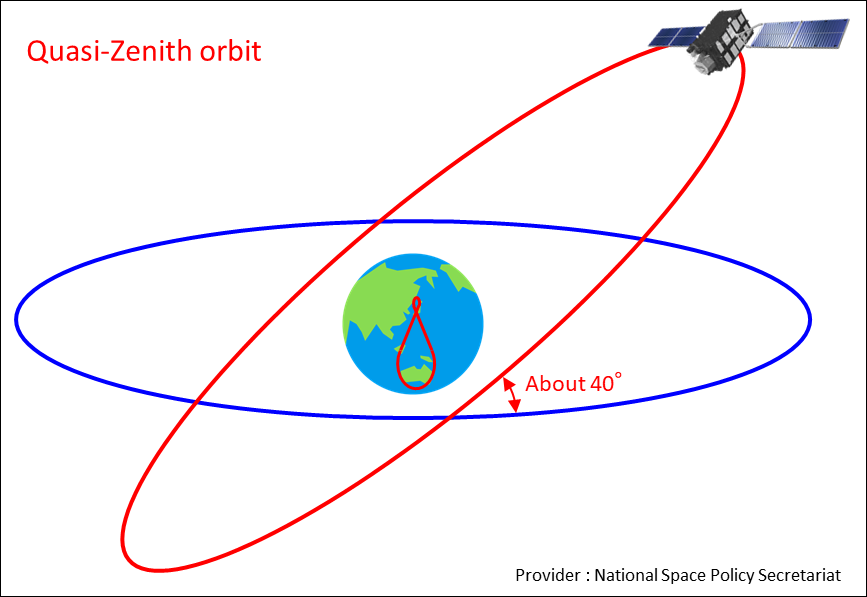
2.Mobile Satellite Communication System by the Quasi-Zenith Satellite
The quasi-zenith satellite is an artificial satellite of the satellite system where one satellite always stays near the zenith in Japan by positioning at least three satellites synchronously on the orbit inclined at 45 degrees from the geostationary orbit. As the ground surface orbit draws the shape of number 8, it's also called "Number 8 Orbit Satellite". It can obtain a high elevation angle to reduce the influence of buildings and so forth (blocking.)
- i.Altitude: about 32,000-40,000 km
- ii.Orbit: circle orbit crossing with the equator by the angle of about 40-50 degrees
- iii.Number of Satellites: 3
- iv.Principal Mobile Satellite Communications System: QZS-1, QZS-2, QZS-4
3.Mobile Satellite Communication System by the Non-Geostationary Satellite
This is roughly divided into three kinds of orbits: highly elliptic orbit, medium earth orbit, and low earth orbit. The medium and low earth orbits have lower satellite altitudes to shorten the radio transmission delay, enabling more speedy and smooth communication. Specifically, the highly elliptic orbit can obtain a higher elevation angle. It is currently being researched and developed.
- i.Highly Elliptic Orbit (HEO)
- Altitude: about 500-40,000km
- Orbit: about 12 hours
- Number of Satellites: 4 or more
- Principal Satellite System: Molniya
- ii.Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Altitude: about 2,000-36,000km
- Orbit: about 5-6 hours
- Number of Satellites: several dozen (for the entire world)
- Principal Satellite System: GPS
- iii.Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Altitude: 500km - 2,000 km
- Orbit: about 5-6 hours
- Number of Satellites: several dozen (for the entire world)
- Principal Mobile Satellite Communications System: IRIDIUM, Globalstar, Orbcomm

